If someone undergoes surgery or comes out of any long-term illness, they are recommended to go on a diet that can fulfill their nutritional needs without causing them discomfort. Soft diet and Mechanical soft diet are the diets that are designed to meet the needs of such people. While both diets are highly nutritious and health-friendly, there are a few differences between both that one needs to look out for.
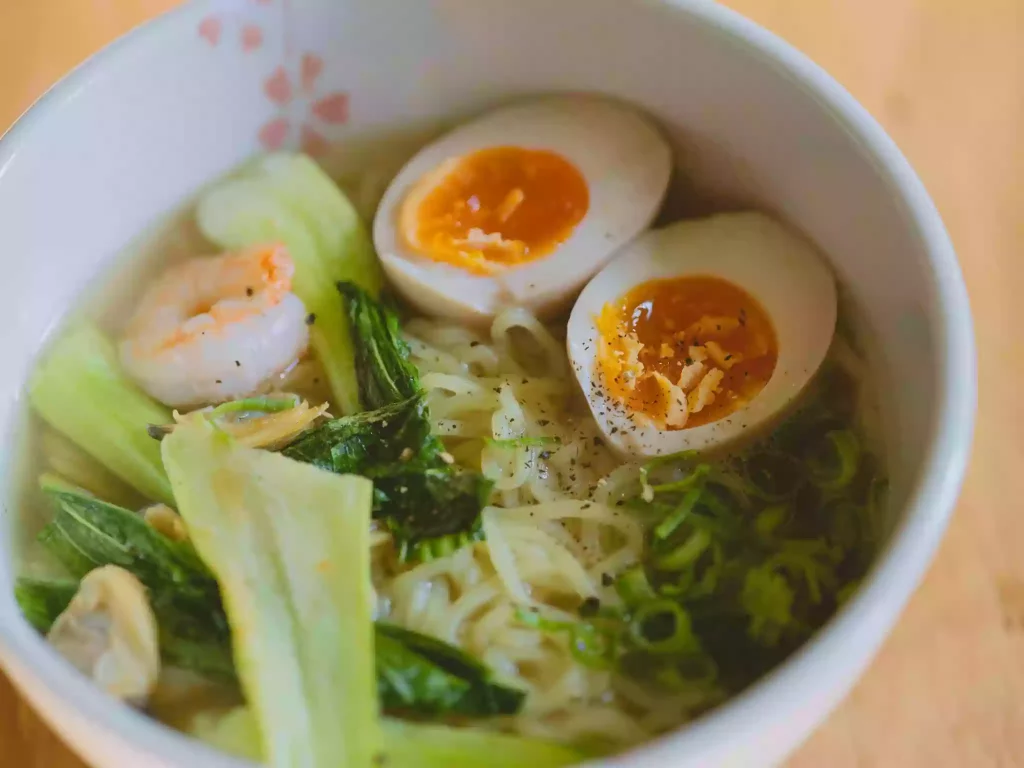

What is a soft diet?
A soft diet is based on eating soft foods that are easy to chew and swallow and is recommended by physicians for recovery from surgery or an illness. It needs to be followed for a week or more based on the recovery speed. It is also recommended for people who experience dental issues and cannot chew solid foods in their original form. These foods are then boiled or mashed to create soft foods that are easy on teeth and stomach.
What is a mechanical soft diet?
A mechanical soft diet can be considered a sister of the soft diet, as it shares a lot of similarities with the soft diet. It’s called a mechanical soft diet because food items that need to be consumed are made smooth-textured by mechanical ways like blending and grinding.
Difference between soft and mechanical soft diet
These diets are almost identical to each other, with few exceptions in the food department, like what to eat and what not to. Let’s take a look if they look any different or not.
As a soft diet is more inclined toward recovery, it restricts the consumption of hard to chew or swallow foods like raw vegetables and fruits, meat slices, chewy bread, and undercooked legumes. Sometimes, it is also recommended to avoid the intake of high-fiber foods like cereals and whole-grain bread. To improve the recovery of the patients, it also put restrictions on the use of gas-causing foods like broccoli, to ease the digestion of foods. For a similar reason, fried, spicy, and greasy foods are also kept off-limits.
To soften the texture of foods, mashing and cooking are followed in a soft diet. It is recommended to use canned or soft-cooked vegetables in place of raw vegetables. Only those fruits are allowed which have a soft texture and their skin needs to peel off. Soaked cereals and refined bread are preferred over whole-grain bread. To consume the meat and poultry, it is advised to cook it to get a tender state and the meat should be moist enough to get swallowed easily.
As compared to a soft diet, a mechanical soft diet is more inclined towards the people suffering from any dental issues, mouth diseases, dysphagia, narrowing of the esophagus, or recovering from the mouth surgery– that makes it hard for them to chew or swallow food. That’s why a mechanical soft diet is focused on changing the texture and consistency of the food. It also does not put any restriction on the consumption of fiber-rich foods, spices, fat, or seasonings.
To change the consistency and texture, fruits and vegetables are soft-cooked or pureed. Other food items like meat, poultry, and fish are usually well-cooked, grounded, or moistened with gravy, which makes them chewable. Cereals are consumed after being soaked in milk or water and legumes are allowed to eat only after boiling. Dairy products with soft textures are recommended.
Which one is better?
These diets are designed to help the ones suffering from illness or recovering from it, so there is no good or bad among them. It solely depends on your medical condition and the recommendation of your physician. Both diets provide nutritional content and maintain an intake of soft food as well.
Conclusion
Whether a soft diet or a mechanical soft diet, both need to be followed strictly to reap the benefits and to get recovered from the surgery or a disease, as soon as possible. If you need to follow these diets for the long term, it’s better to ask your physician to recommend alternatives for the missing nutrients. A lack of essential or micronutrients can cause health issues.

I look up to fitness as a lifestyle and love to pen down about it. I have 2 years of experience in content writing and I am here to share my research and knowledge on health and fitness.